Project Overview
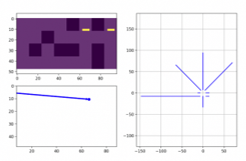
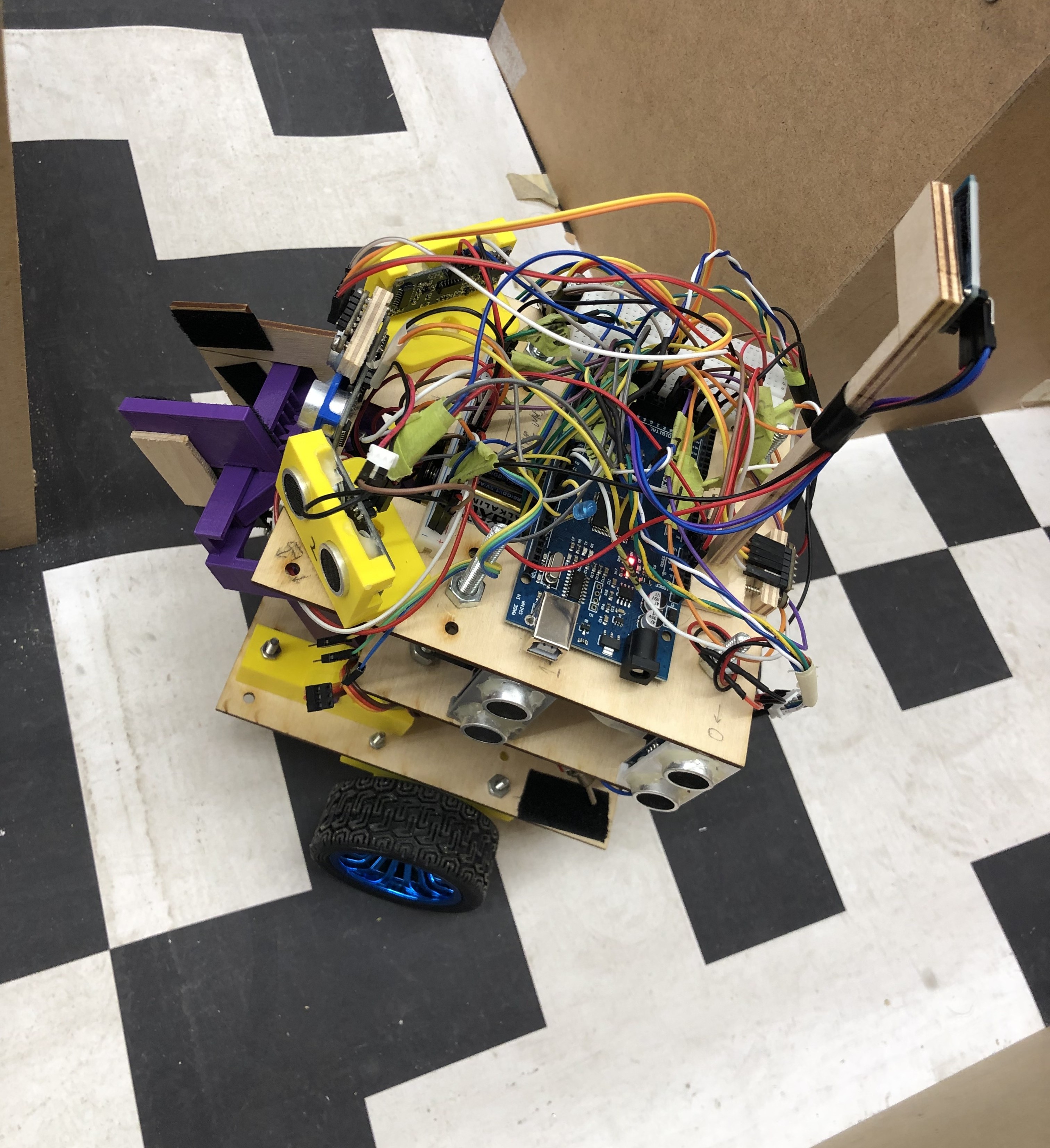
This project aimed to build a fully autonomous rover capable of navigating a predefined maze, detecting blocks, and transporting them to a target location without human intervention. The rover used multiple ultrasonic, IR and ToF sensors, and Python control logic. Localization was achieved using Monte Carlo Localization (MCL), where range sensor measurements were compared against an occupancy grid map to estimate position and orientation. Although the complete maze run took over nine minutes, the system successfully demonstrated end-to-end autonomy including obstacle avoidance, localization, and block transport.

My Contributions
-
I designed and assembled the hardware platform, implemented the sensor integration pipeline, and programmed the localization and control algorithms. Specifically, I configured and calibrated the sensor array, applied MCL for position estimation, and developed motion control logic in Python to complete maze navigation tasks.
Technologies
Tools: Python · Auduino Mega · Monte Carlo Localization(MCL) · Ultrasonic and ToF sensors · Path Planning
Platform: Auduino + Python
What I Learned
I learned how to implement a probabilistic localization algorithm (MCL) in practice, how to fuse multiple sensor readings for reliable navigation, and how to integrate mechanical design with perception and control in a full robotic system. The project also highlighted the trade-offs between algorithm robustness and runtime efficiency when deployed on limited hardware.